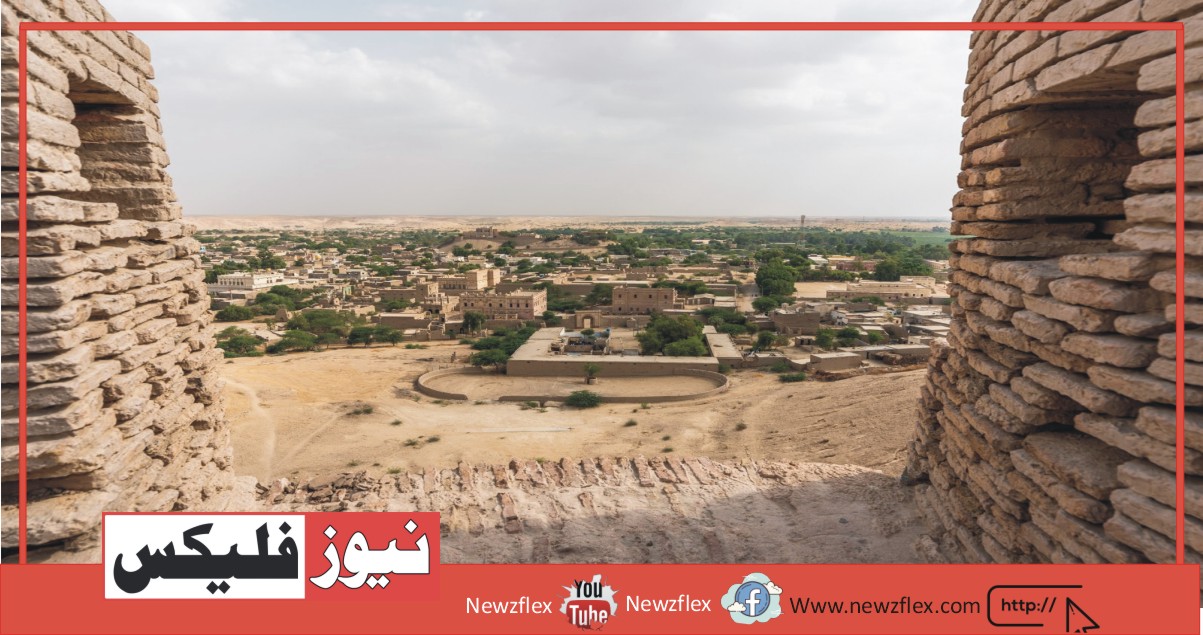
Taxila
Taxila city is 35 km, which is a 20-minute drive from Islamabad towards the northwest where the civilization of Gandhara exists. Taxila original name was Takshasila. After being destroyed 3 times by the world quake it absolutely was made earthquake-proof. Its name was changed from Takshasila to Taxila where the word tax means to cut and sila means a stone cut of the stone city.
Taxila is one of richest South Asia archeologist site.
Taxila is a testament to Buddhism. Buddha himself spent 40 years of life traveling and teaching in this part of Pakistan and lots of saying that it’s from here the fashionable Buddhism takes its roots. The Greeks came to Taxila under the banner of the conqueror, Alexander the good.
Buddhism religion finds its roots in the subcontinent so it’s not surprising that a number of the most effective archeologist figures for Buddhism are in Pakistan. Taxila is one of the best.
Taxila Museum
Taxila Museum has located 35 km from Islamabad on the Grand highway to Peshawar. The founding father of the museum is Sir chief justice, who was then the Director General of Archeology in India. He was behind the Greek-style concept of the museum.
It has many significant findings from the Taxila site. And are probably a few museums in the world that tell the story of Europe meeting the region. The museum is most noted for its Buddhist sculpture with features that were created when Alexander the nice visited here some 2400 years ago.
This is a site museum and its collection consists of objects from the period 600 B.C to 500 AD. associated with Buddhist, Hindu, and Jain religions objects discovered in three ancient cities are more than twenty Buddhist stupas and monasteries, and Greek temples. The gathering of Stone Buddhist sculptures from the first to the seventh centuries in Pakistan is named Gandharan Art. There are 5000 objects displayed, including stone, stucco, terracotta, silver, gold, iron, and semiprecious stones.
The material has been presented in the six galleries of the museum. In the middle of the halls are table showcases & other objects are exhibited in the wall showcases also.
As we enter the museum, there’s a main big hall, which contains a complete stupa from the Buddhist monastery of Mohra Moradu to showcase. An archaeological map of Taxila is present on its left side. Table showcases exhibit small finds. The wall showcases schist stone sculptures on the 2 sides. The museum presents scenes from the lifetime of mysticism and samples of Gandharan Art. Red sandstone sculptures and two sandstone sculptures have also been displayed.
The second hall to the left has stucco sculptures from Mohra Moradan in the wall showcases and Buddhist sculptures brought from the Julian monastery. On the ground are glazed tiles of the Kushana period. In the third hall, they need stucco heads on the hall showcases. The heads show different faces and hairstyles. the large Buddha heads are typically Gandharan in style.
Through the most hall, we are able to enter a little fourth hall, which has silver and gold jewelry and coins of the local kings on display. The gold jewelry is in foreign furthermore as local styles.
In the fifth small hall, the first object is an Aramaic inscription of King Asoka. Then we see a series of inscriptions written in Kharoshthi and also in Brahmi on paper. Then we see small terracotta figurines and a small terra cotta ceremonial tank model. On the other wall, there are iron objects; arrowheads, nails, horse strips, and plough.
Finally, after we enter the last sixth hall, on the wall showcases we see silver glasses of various shapes, bowls, spoons, toilet trays, small pottery pieces, bowls, and plates of terracotta and pottery arranged for distillation. On the ground are big storage jars, pestle and mortar, and saddle querns.
It is one of the most effective museums in the whole world. Its timings are from 8 30 to 530 in summer and from 9-4 in winter.
SIRKAP
The Greeks came to Taxila under the banner of the conqueror, Alexander the great. They built Taxila 1st city and called it Sirkap. The city was the first of its kind in South Asia using the same building style that was found in the Asian Greek capital of Athens. Today all that is left is roads and building foundations. Sirkap history spends over 1000 years which involves different empires conquering and rebuilding it.
It is the second major ancient city in Taxila. It is known as Sirkap after the name of a wicked character of a folk legend, “Raja Rasalu and seven demons” that is said to have lived on this site. The excavation of this old city was carried out by H. Hargreaves during 1912-1930 under the direction of Sir John Marshall and in 1944-45 by Sir Mortimer Wheeler and his colleagues.
Sirkap is part of the larger archaeological complex at Taxila, now located in the modern state of Pakistan, in the province of Punjab. The archaeological complex at Taxila, of which Sirkap is one site, is located about 22 kilometers to the west of Islamabad, and about 25 kilometers to the northwest of the city of Rawalpindi.
The great city was one time termed the greatest university for law, history, and medicine on the subcontinent. And the ancient city’s architectural design plans were so ahead of their time that it was put to use when Islamabad was built some 50 years ago.
It was a well-planned city Islamabad is built on this design. It has 2 cities beneath it which are still to be judged. When in 1912 digging was carried out, just to show the signs of 2 cities under it, on one corner of the city 3 layers were dug which represents 3 periods
Archaeologists have identified three phases:
1-The first, Demetrian phase of the Greek city, second century AD.(picture, bottom)
2- The Saca period, until an earthquake in ca. 30 CE. (Picture, center)
3- The Parthian period (picture, thin layer at the top).
The city is heavily influenced by Greek city planning principles. The streets of the city were more regular than those at Bhir, and the houses were mostly made of coursed stone. There were temples, houses, shrines, and stupas. A stupa is a funeral mound, usually associated with the death and nirvana of Buddha. Buddhists always were the main religious group, and we find many stupas in Sirkap.
A straight line, dividing the 1200 m long towns into two halves. The private houses were constructed of rubble masonry covered with mud plaster. Usually, they had a small court, a second floor, and a flat roof. After the earthquake that marks the break between the Indo-Scythian and Indo-Parthian periods, many houses were rebuilt with stronger walls and deeper foundations.
THE MAIN ROAD OF SIRKAP
The city is dominated by the main street along, which small rooms are meant for shops. As we enter the gateway, we see the refuse walls just inside, and then the passage bends and we have the inner guard rooms before we reach the main street.
Sun Temple
There were sakas people who believed in the sun god. When the city was dug, a statue of a sun god was found. When Parthian came they changed the place and used it as a sundial. It’s been called a “SUN TEMPLE” because the residents used it to know the timing, standing in front of the temple to see where the shadow of the sun comes from different angles and identify the timings.
Round Stupa
On the left side of the Sun temple, there is the solid drum of a round stupa, which is also called a private stupa because it was built in a house. When it was dug, the statue of a dancer was found Raqasa.
Apsidal Temple
After the earthquake that destroyed the city in 30 AD, the Buddhist shrine was built in the spacious courtyard. The round part was probably in use for a small stupa, but no traces of it remain.
Jain Temple
It is a sect of Hindus who believe in a Mahaveer. When Mahaveer died his ashes were divided into different parts. One part of the ashes are inside it. When the city was drugged, some temples of Mahaveer were found which are now in the Taxila museum. Some inscriptions regarding the Jain mark were also found.
Juliann Buddhist Monastery
Its real name was Jaye Walian means place of Walian. It is included in the Gandharan civilization as one of the best educational cities. People from different parts of the world used to come here to learn Buddhism.
Buddha sculptures found there were more than anywhere and were in better condition. Before 600 BC Julian University was at its peak. It was created on a top hill mountain which was 100 m above the ground. What is left over now, one can find signs of the kitchen, bathrooms dining room, and places of worship there. Many stupas were built here. Places of worship are covered with roofs of steel. At that time whenever monks people used to come here to worship the main stupa then just as a favor before going back they used to build one small stupa. Here statues of Yunnan god Atlantes are also found about which it is said that he is holding skies on his own shoulders.
The main statue of Julian which is the mahatma statue is known as a statue for health, people of Buddhism believe that when an ill person out his finger on the belly button of it and prays for his health then he gets fit. Around the main stupa, there are about 21 more stupas Julian University was burned by Mongol tribes in the 400 century and after 1000 years these signs were found by South Korean experts. By promoting Historical places like Julian, tourism can be enhanced which in turn will also help Pakistan’s economy.
Dharmarajika Stupa (2nd century AD)
The earliest Buddhist monument in Pakistan. It’s an archeological site situated about 2km from Taxila Museum.
It was built by Asoka to enshrine the relics of lord Buddha at the time of its re-distribution to enshrine them in a number of other stupas at different places, it is preferred that king Asoka opened 7 original old stupas and collected mementos to accept thousand of stupas and dharmarajika stupa is one of them.
The stupa is situated in a circular structure and is about 15 meters high, raised on a plate form.
The passage to the ruins at the hillock from the main road is very fine and lush green with lots of trees and there seems to be a small stream from the old times of Asoka, used for water supply to the resident of the shrine and monastic areas.
Dharmarajika Stupa is one of eight shrines constructed in the 3rd century BC during the reign of Emperor Asoka of the Mauryan dynasty to house relics of the Buddha. The shrine gradually expanded, reaching its largest size in the 2nd century A.D. Now a ruin, the stupa was once coated with lime plaster and gilding, though these have fallen away along with a seven-tier umbrella stone that once crowned the top. Near the stupa are the remains of vast monasteries that are barely distinguishable but for the foundation stones
Shrine of Double Headed Eagle :
There is a double-headed eagle shrine along the main street of sirkap. Nobody knows its original name. It is called the shrine of the double-headed eagle because of the bird on the arch that has two heads. Alexander’s army also left a cultural imprint on this shrine. The pediment of the shrine is of classical greek architecture. Indian cultural influence can also be seen especially on the outer side of the shrine.
Bhirmound :
The ruins of the city were first discovered in 1913 – 1925 by Sir John Marshall and it continued up till 2002 by different archeologists. The ruins form a town of irregular shape. Bhirmound remained a very important city as it was the center of administration, education, and trade. Buddhism became an important religion during the period of Ashoka – The grandson of Chandragupta. It was also the provincial capital during the Mauryan dynasty.
Jandial Temple :
It is one of the most unique buildings in Central Asia. It closely follows the structure of classical temples of Greece. It consists of a central shrine with four Ionic columns supporting a porch. Two variations are noted in the temple layout at Jandial:
Firstly, the roof of the temple was supported by a wall that had 20 windows instead of the Greek colonnade.
Secondly, the place of the tower was traditionally reserved for a chapel. It is probably the only or at least one of the very few greek temples in the subcontinent.
Nicholson Monument :
There comes a monument en route to the historical city of Taxila. The monument was constructed in honor of brigadier general Nicholson who was a famous British military figure. It is situated at the Tarnol pass or Margalla Pass. It was constructed in 1868. It is about 40 feet high monument. There is also a small memorial fountain at the base of the hillock on which the Memorial stands. Besides these places, there are also no. of other places that can be visited while one is in Taxila. No. of good restaurants, hotels, and motels have been built and they provide good facilities. E.g Ghandhara hotel, Ghandhara restaurant, PTDC motel.
There are also Hindu temples located in the heart of town. These were the temples built by Ram rakhi in memory of her husband Bhagat Lal.
The Bottom Line:
Taxila is a ‘ city of secrets and rich history ‘
ٹیکسلا
ٹیکسلا شہر 35 کلومیٹر اسلام آباد سے شمال مغرب کی طرف 20 منٹ کی مسافت پر ہے جہاں گندھارا کی تہذیب موجود ہے۔
ٹیکسلا کا اصل نام تکسلا تھا۔ زلزلے سے 3 بار تباہ ہونے کے بعد اسے زلزلہ پروف بنایا گیا۔ اس کا نام تکشاشیلا سے بدل کر ٹیکسلا رکھ دیا گیا جہاں لفظ ٹیکس کا مطلب ہے کاٹنا اور سیل کا مطلب پتھر کا شہر ہے۔
ٹیکسلا جنوبی ایشیا کے امیر ترین آثار قدیمہ کی جگہوں میں سے ایک ہے۔ ٹیکسلا بدھ مت کا ثبوت ہے۔ خود بدھا نے زندگی کے 40 سال پاکستان کے اس حصے میں سفر اور تعلیم دیتے ہوئے گزارے اور بہت سے لوگوں کا کہنا ہے کہ یہیں سے جدید بدھ مت کی جڑیں ملتی ہیں۔ یونانی فاتح سکندر اعظم کے جھنڈے تلے ٹیکسلا آئے۔
بدھ مت مذہب کی جڑیں برصغیر میں پائی جاتی ہیں اس لیے یہ حیرت کی بات نہیں ہے کہ بدھ مت کے لیے چند بہترین آثار قدیمہ کی شخصیات پاکستان میں ہیں۔ ٹیکسلا سب سے بڑے میں سے ایک ہے۔
ٹیکسلا میوزیم
ٹیکسلا میوزیم اسلام آباد سے پشاور تک گرینڈ ٹرنک روڈ پر 35 کلومیٹر کے فاصلے پر واقع ہے۔ میوزیم کے بانی سر جان مارشل ہیں، جو اس وقت ہندوستان میں آثار قدیمہ کے ڈائریکٹر جنرل تھے۔ وہ میوزیم کے یونانی طرز کے تصور کے پیچھے تھا۔
اس میں ٹیکسلا سائٹ سے بہت سی اہم دریافتیں ہیں۔ اور شاید دنیا کے چند ایسے عجائب گھر ہیں جو یورپ کے مشرق بعید سے ملنے کی کہانی بیان کرتے ہیں۔ میوزیم اپنے بدھ مت کے مجسمے کے لیے سب سے زیادہ مشہور ہے جس کی خصوصیات تقریباً 2400 سال قبل سکندر اعظم کے یہاں آنے کے وقت بنائی گئی تھیں۔
یہ ایک سائٹ میوزیم ہے اور اس کا مجموعہ 600 قبل مسیح سے 500 اے ڈی تک کی اشیاء پر مشتمل ہے۔ بدھ، ہندو اور جین مذاہب سے متعلق تین قدیم شہروں سے دریافت ہونے والی اشیاء میں بیس سے زائد بدھ اسٹوپا اور خانقاہیں اور یونانی مندر ہیں۔ پاکستان میں پہلی سے ساتویں صدی تک پتھر کے بودھ مجسمے کا مجموعہ گندھارن آرٹ کہلاتا ہے۔ یہاں 5000 اشیا رکھی گئی ہیں جن میں پتھر، سٹوکو، ٹیراکوٹا، چاندی، سونا، لوہا اور نیم قیمتی پتھر شامل ہیں۔
اس مواد کو میوزیم کی چھ گیلریوں میں پیش کیا گیا ہے۔ ہالوں کے بیچوں بیچ ٹیبل شوکیس ہیں اور دیوار کے شوکیس میں بھی دیگر اشیاء کی نمائش کی گئی ہے۔
جیسے ہی ہم میوزیم میں داخل ہوتے ہیں، وہاں ایک بڑاہال ہے، جس میں نمائش کے لیے موہرا موراڈو کی بدھ خانقاہ کا ایک مکمل اسٹوپا ہے۔ ٹیکسلا کا آثار قدیمہ کا نقشہ اس کے بائیں جانب موجود ہے۔ ٹیبل شوکیس چھوٹے تلاشوں کی نمائش کرتے ہیں۔ دیوار پر دونوں اطراف میں پتھر کے مجسمے دکھائے گئے ہیں۔ میوزیم بدھ کی زندگی کے مناظر اور گندھارن آرٹ کی مثالیں پیش کرتا ہے۔ سرخ ریت کے پتھر کے مجسمے، دو ریت کے پتھر کے مجسمے بھی آویزاں کیے گئے ہیں۔
بائیں جانب دوسرے ہال میں دیوار کی نمائش میں موہرا مورادن کے سٹوکو مجسمے اور جولین خانقاہ سے لائے گئے بدھ مجسمے ہیں۔ فرش پر کشانا دور کی چمکیلی ٹائلیں ہیں۔ تیسرے ہال میں ان کے ہال کے شوکیس پر سٹوکو سر ہیں۔ سر مختلف چہرے اور بالوں کے انداز دکھاتے ہیں۔ بدھا کے بڑے سر عام طور پر گندھارن کے انداز میں ہوتے ہیں۔
مرکزی ہال کے ذریعے، ہم ایک چھوٹے سے چوتھے ہال میں داخل ہو سکتے ہیں، جس میں چاندی اور سونے کے زیورات اور مقامی بادشاہوں کے سکے رکھے ہوئے ہیں۔ سونے کے زیورات غیر ملکی اور مقامی انداز میں ہیں۔
پانچویں چھوٹے ہال میں پہلا اعتراض بادشاہ اشوکا کا ایک آرامی نوشتہ ہے۔ پھر ہم کاغذ پر خروشتھی اور براہمی میں بھی لکھے ہوئے نوشتہ جات کا ایک سلسلہ دیکھتے ہیں۔ پھر ہم ٹیراکوٹا کے چھوٹے مجسمے اور ایک چھوٹا سا ٹیرا کوٹا رسمی ٹینک کا ماڈل دیکھتے ہیں۔ مخالف دیوار پر لوہے کی چیزیں ہیں۔ تیر کے نشان، ناخن، گھوڑے کی پٹیاں اور ہل بھی موجود ہیں۔
آخر کار جب ہم آخری چھٹے ہال میں داخل ہوتے ہیں تو دیوار کے شوکیس پر ہمیں مختلف شکلوں کے چاندی کے شیشے، پیالے اور چمچے، بیت الخلا کی ٹرے، مٹی کے برتنوں کے چھوٹے چھوٹے ٹکڑے، پیالے اور ٹیراکوٹا کی پلیٹیں اور مٹی کے برتنوں کو کشید کرنے کا انتظام نظر آتا ہے۔ فرش پر بڑے بڑے سٹوریج جار، پیسٹل اور مارٹر اور سیڈل کے کورن ہیں۔
یہ پوری دنیا کے بہترین میوزیم میں سے ایک ہے۔ اس کے اوقات گرمیوں میں 8 سے 530 اور سردیوں میں 9-4 ہوتے ہیں۔
سرکیپ
یونانی فاتح سکندر اعظم کے جھنڈے تلے ٹیکسلا آئے۔ انہوں نے ٹیکسلا پہلا شہر بنایا اور اسے سرکپ کہا۔ یہ شہر جنوبی ایشیا میں اپنی نوعیت کا پہلا وہی عمارتی طرز استعمال کرتا تھا جو ایشیائی یونانی دارالحکومت ایتھنز میں پایا جاتا تھا۔ آج صرف سڑکیں اور تعمیراتی بنیادیں رہ گئی ہیں۔ سرکیپ کی تاریخ 1000 سال سے زیادہ پر محیط ہے جس میں مختلف سلطنتوں کو فتح کرنا اور اسے دوبارہ تعمیر کرنا شامل ہے۔
یہ ٹیکسلا کا دوسرا بڑا قدیم شہر ہے۔ اسے ایک لوک لیجنڈ، ‘راجہ رسالو اور سات بدروحوں’ کے ایک شریر کردار کے نام سے سرکپ کہا جاتا ہے جس کے بارے میں کہا جاتا ہے کہ وہ اس جگہ پر رہتے تھے۔ اس پرانے شہر کی کھدائی ایچ. ہارگریوز نے 1912-1930 کے دوران سر جان مارشل کی ہدایت پر اور 1944-45 میں سر ماٹائمر وہیلر اور ان کے ساتھیوں نے کی تھی۔
سرکاپ ٹیکسلا کے بڑے آثار قدیمہ کے احاطے کا حصہ ہے، جو اب پاکستان کی جدید ریاست پنجاب کے صوبے میں واقع ہے۔ ٹیکسلا میں آرکیالوجیکل کمپلیکس، جس میں سرکپ ایک جگہ ہے، اسلام آباد کے مغرب میں تقریباً 22 کلومیٹر اور راولپنڈی شہر کے شمال مغرب میں تقریباً 25 کلومیٹر کے فاصلے پر واقع ہے۔
عظیم شہر کو ایک زمانے میں برصغیر میں قانون، تاریخ اور طب کی سب سے بڑی یونیورسٹی کہا جاتا تھا۔ اور قدیم شہر کے آرکیٹیکچرل ڈیزائن کے منصوبے اپنے وقت سے اتنے آگے تھے کہ اسلام آباد کو تقریباً 50 سال قبل تعمیر کرتے وقت استعمال میں لایا گیا تھا۔ یہ ایک منصوبہ بند شہر تھا جس کے ڈیزائن پر اسلام آباد تعمیر کیا گیا ہے۔ اس کے نیچے 2 شہر ہیں جنہیں کھودنا ابھی باقی ہے۔ جب 1912 میں کھدائی کی گئی تو صرف اس کے نیچے 2 شہروں کی نشانیاں دکھانے کے لیے شہر کے ایک کونے پر 3 پرتیں کھودی گئیں جو 3 ادوار کی نمائندگی کرتی ہیں۔
ماہرین آثار قدیمہ نے تین مراحل کی نشاندہی کی ہے۔
نمبر1- یونانی شہر کا پہلا، ڈیمیٹرین مرحلہ، دوسری صدی عیسوی۔ (تصویر، نیچے)
نمبر2- ساکا دور میں زلزلہ آنے تک۔ 30 عیسوی (تصویر، مرکز)
نمبر3- پارتھین دور (تصویر، اوپر کی پتلی تہہ)۔
یہ شہر یونانی شہر کی منصوبہ بندی کے اصولوں سے بہت زیادہ متاثر ہے۔ شہر کی گلیاں بھیر کی نسبت زیادہ منظم تھیں اور گھر زیادہ تر پتھر کے بنے ہوئے تھے۔ مندر، گھر، مزار اور سٹوپا تھے۔ سٹوپا ایک جنازے کا ٹیلہ ہے، جو عام طور پر بدھ کی موت اور نروان سے منسلک ہوتا ہے۔ بدھ مت ہمیشہ اہم مذہبی گروہ تھے، اور ہمیں سرکاپ میں بہت سے سٹوپا ملتے ہیں۔
ایک سیدھی لکیر، جو 1200 میٹر طویل شہر کو دو حصوں میں تقسیم کرتی ہے۔ نجی مکانات مٹی کے پلاسٹر سے ڈھکے ملبے کی چنائی سے بنائے گئے تھے۔ عام طور پر، ان کی ایک چھوٹی سی عدالت، دوسری منزل اور ایک فلیٹ چھت ہوتی تھی۔ اس زلزلے کے بعد جو انڈو-سائیتھین اور انڈو پارتھین ادوار کے درمیان وقفے کی نشاندہی کرتا ہے، بہت سے مکانات مضبوط دیواروں اور گہری بنیادوں کے ساتھ دوبارہ تعمیر کیے گئے۔
سرکاپ کی مرکزی سڑک
شہر میں مرکزی سڑک کے ساتھ ساتھ اس کا غلبہ ہے، جس میں چھوٹے کمرے دکانوں کے لیے ہیں۔ جیسے ہی ہم گیٹ وے میں داخل ہوتے ہیں، ہمیں نظر آتا ہے کہ دیواریں بالکل اندر ہی اندر سے جھکتی ہوئی نظر آتی ہیں، اور مرکزی سڑک پر پہنچنے سے پہلے ہمارے پاس اندرونی محافظ کے کمرے ہیں۔
سورج مندر
ساکا لوگ سورج دیوتا کو مانتے تھے۔ جب شہر کی کھدائی کی گئی تو ایک سورج دیوتا کی مورتی ملی۔ جب پارتھین آئے تو انہوں نے جگہ بدل دی اور اسے سن ڈائل کے طور پر استعمال کیا۔ اسے ‘سن ٹیمپل’ کہا جاتا ہے کیونکہ رہائشیوں نے اسے وقت جاننے کے لیے استعمال کیا، مندر کے سامنے کھڑے ہو کر یہ دیکھنے کے لیے کہ سورج کا سایہ مختلف زاویوں سے کہاں آتا ہے اور اوقات کی شناخت کرتے ہیں۔
گول اسٹوپا
سورج مندر کے بائیں جانب ایک گول اسٹوپا کا ٹھوس ڈھول ہے جسے پرائیویٹ اسٹوپا بھی کہا جاتا ہے کیونکہ یہ ایک گھر میں بنایا گیا تھا۔ کھدائی کی گئی تو رقاصہ کا مجسمہ ملا
اپسائیڈل مندر
تیس عیسوی میں شہر کو تباہ کرنے والے زلزلے کے بعد بدھ مت کی عبادت گاہ کو کشادہ صحن میں بنایا گیا تھا۔ گول حصہ غالباً ایک چھوٹے سٹوپا کے استعمال میں تھا، لیکن اس کا کوئی نشان باقی نہیں رہا۔
جین مندر
یہ ہندوؤں کا ایک فرقہ ہے جو مہیوئر پر یقین رکھتا ہے۔ جب مہاویر کی موت ہوگئی تو اس کی راکھ کو مختلف حصوں میں تقسیم کیا گیا تھا۔ راکھ کا ایک حصہ اس کے اندر ہے۔ جب شہر کو کھودیا گیا تو ، مہاویر کے کچھ مندر ملے جو اب ٹیکسلا میوزیم میں ہیں۔ جین مارک سے متعلق کچھ شلالیھ بھی ملے تھے
جولیان بدھ مت کی خانقاہ
اس کا اصل نام جئے ولیان کا مطلب ہے والین کی جگہ۔ یہ گندھارن تہذیب میں ایک بہترین تعلیمی شہر میں سے ایک کے طور پر شامل ہے۔ دنیا کے مختلف حصوں سے تعلق رکھنے والے لوگ بدھ مت کو سیکھنے کے لئے یہاں آتے تھے۔
یہاں پائے جانے والے بدھ کے مجسمے کہیں سے کہیں زیادہ تھے اور بہتر حالت میں تھے۔ اس سے پہلے کہ 600 قبل مسیح میں جولین یونیورسٹی عروج پر تھی۔ یہ ایک اوپر پہاڑی پہاڑ میں بنایا گیا تھا جو زمین سے 100 میٹر بلندی پر تھا۔ اب کیا چھوڑ دیا گیا ہے ، کسی کو باورچی خانے ، باتھ رومز ڈائننگ روم اور وہاں عبادت گاہ کے آثار مل سکتے ہیں۔ یہاں بہت سارے اسٹوپا بنائے گئے تھے۔ عبادت کے مقامات اسٹیل کی چھتوں سے ڈھکے ہوئے ہیں۔ اس وقت جب بھی راہبوں کے قسم کے لوگ یہاں واپس جانے سے پہلے ہی ایک احسان کی حیثیت سے مرکزی اسٹوپا کی پوجا کرنے آتے تھے تو وہ ایک چھوٹا سا اسٹوپا تعمیر کرتے تھے۔ یہاں یونان گاڈ اٹلانٹس کے مجسمے بھی پائے گئے ہیں جن کے بارے میں کہا جاتا ہے کہ وہ اپنے کندھوں میں آسمان رکھتا ہے۔
جولین کا اہم مجسمہ جو مہاتما مجسمہ ہے اسے مجسمہ برائے صحت کے نام سے جانا جاتا ہے ، بدھ مت کے لوگوں کا خیال ہے کہ جب ایک بیمار شخص اس کے پیٹ کے بٹن میں اپنی انگلی نکالتا ہے اور اس کی صحت کے لئے دعا کرتا ہے تو وہ فٹ ہوجاتا ہے۔ مین اسٹوپا کے آس پاس تقریبا 21 21 اسٹوپاس جولین یونیورسٹی کو 400 صدی میں منگول قبائلی نے جلایا تھا اور 1000 سالوں کے بعد یہ علامتیں جنوبی کوریا کے ماہرین نے پائے تھے۔ جولین جیسے تاریخی مقامات کو فروغ دینے سے ، سیاحت کو بڑھایا جاسکتا ہے جس کے نتیجے میں پاکستان کی معیشت میں بھی مدد ملے گی۔
دھرمارجیکا اسٹوپا (دوسری صدی عیسوی)
پاکستان میں ابتدائی بدھ مت کی یادگار۔ یہ ٹیکسیلا میوزیم سے 2 کلومیٹر دور واقع ایک آثار قدیمہ کی جگہ ہے۔
اسوکا نے لارڈ بدھ کے اوشیشوں کو اپنی دوبارہ تقسیم کے وقت مختلف جگہوں پر متعدد دیگر اسٹوپوں میں شامل کرنے کے لئے انشرائن کرنے کے لئے بنایا تھا ، اس بات کا حوالہ دیا جاتا ہے کہ شاہ اسوکا نے 7 اصلی پرانے اسٹوپاس کھولے اور ہزاروں کو قبول کرنے کے لئے میمنٹو جمع کیا۔ اسٹوپاس اور دھرمارجیکا اسٹوپا ان میں سے ایک ہیں۔
اسٹوپا ایک سرکلر ڈھانچے میں واقع ہے اور تقریبا 15 15 میٹر اونچائی پر ہے ، جو پلیٹ کی شکل پر اٹھایا جاتا ہے۔
مین مین روڈ سے پہاڑی کے کھنڈرات کی طرف جانے والا راستہ بہت ٹھیک اور سرسبز سبز ہے جس میں بہت سارے درخت ہیں اور ایسا لگتا ہے کہ اسوکا کے پرانے زمانے سے ایک چھوٹی سی ندی ہے ، جو مزار کے رہائشی کو پانی کی فراہمی کے لئے استعمال کرتی تھی
دھرمارجیکا اسٹوپا تیسری صدی قبل مسیح میں موریئن خاندان کے شہنشاہ اسوکا کے دور میں بدھ کے اوشیشوں کے ریلکس کے دور میں تعمیر کردہ آٹھ مزارات میں سے ایک ہے۔ مزار آہستہ آہستہ پھیل گیا ، دوسری صدی عیسوی میں اس کے سب سے بڑے سائز تک پہنچ گیا۔ اب ایک بربادی ، اسٹوپا کو ایک بار چونے کے پلاسٹر اور گولڈنگ کے ساتھ لیپت کیا گیا تھا ، حالانکہ یہ سات درجے کی چھتری پتھر کے ساتھ ساتھ گر چکے ہیں جس نے ایک بار اوپر کا تاج پوشی کیا تھا۔ اسٹوپا کے قریب وسیع خانقاہوں کی باقیات ہیں جو بمشکل ممتاز ہیں
ڈبل ہیڈ ایگل کے مزار
سرکپ کی مرکزی گلی کے ساتھ ساتھ ایک ڈبل سر ایگل مزار ہے۔ کوئی بھی اس کا اصل نام نہیں جانتا ہے۔ اسے محراب پر پرندوں کی وجہ سے ڈبل ہیڈ ایگل کا مزار کہا جاتا ہے جس کے دو سر ہیں۔ سکندر کی فوج نے بھی اس مزار پر ثقافتی امپرنٹ چھوڑ دیا۔ مزار کا پیڈیمینٹ کلاسیکی یونانی فن تعمیر کا ہے۔ ہندوستانی ثقافت کے اثر و رسوخ کو بھی خاص طور پر مزار کے بیرونی طرف دیکھا جاسکتا ہے۔
بھرماؤنڈ
اس شہر کے کھنڈرات کو پہلی بار 1913 – 1925 میں سر جان مارشل نے دریافت کیا تھا اور یہ 2002 میں مختلف آثار قدیمہ کے ماہرین نے جاری رکھا تھا۔ کھنڈرات فاسد شکل کا ایک قصبہ تشکیل دیتے ہیں۔ بھرماؤنڈ بہت اہم شہر رہا کیونکہ یہ انتظامیہ ، تعلیم ، تجارت کا مرکز تھا۔ چندرگپت کے پوتے اشوکا کے دور میں بھدھزم ایک اہم مذہب بن گیا۔ موریان خاندان کے دوران یہ صوبائی دارالحکومت بھی تھا۔
جینڈیل مندر
یہ وسطی ایشیا کی ایک سب سے منفرد عمارت ہے۔ یہ یونان کے کلاسیکی مندروں کی ساخت کو قریب سے پیروی کرتا ہے۔ اس میں ایک مرکزی مزار پر مشتمل ہے جس میں چار آئنک کالم ہیں جو پورچ کی حمایت کرتے ہیں۔ جینڈیل میں ہیکل کی ترتیب میں دو مختلف حالتوں کا ذکر کیا گیا ہے: سب سے پہلے ، ہیکل کی چھت کو ایک دیوار نے سپورٹ کیا تھا جس میں یونانی نوآبادیات کے بجائے 20 کھڑکیاں تھیں۔ دوم ، ٹاور کی جگہ روایتی طور پر ایک چیپل کے لئے مخصوص تھی۔ برصغیر کے بہت کم یونانی مندروں میں سے شاید یہ واحد یا کم سے کم ہے۔
نیکلسن یادگار
ٹیکسلا کے تاریخی شہر کو شامل کرنے کی ایک یادگار آتی ہے۔ یہ یادگار بریگیڈیئر جنرل نکلسن کے اعزاز میں تعمیر کی گئی تھی جو ایک مشہور برطانوی فوجی شخصیت تھی۔ یہ ترنول پاس یا مارگلا پاس پر واقع ہے۔ یہ 1868 میں تعمیر کیا گیا تھا۔ یہ تقریبا 40 فٹ اونچی یادگار ہے۔ پہاڑی کے اڈے پر ایک چھوٹا سا یادگار چشمہ بھی ہے جس پر یادگار کھڑے ہیں۔ ان مقامات پر ، یہاں بھی نہیں ہے۔ دوسری جگہوں میں سے جن کا دورہ کیا جاسکتا ہے جبکہ ایک ٹیکسلا میں ہے۔ اچھے ریستوراں ، ہوٹلوں اور موٹلز کی تعداد تعمیر کی گئی ہے اور وہ اچھی سہولیات مہیا کرتے ہیں۔ جیسے گندھارا ہوٹل ، گندھارا ریستوراں ، پی ٹی ڈی سی موٹل وغیرہ۔
شہر کے وسط میں ہندو مندر بھی موجود ہیں۔ یہ وہ مندر تھے جو رام راکھی نے اپنے شوہر بھگت لال کی یاد میں بنائے تھے۔
خلاصہ: ٹیکسلا ایک ’راز اور بھرپور تاریخ کا شہر ہے