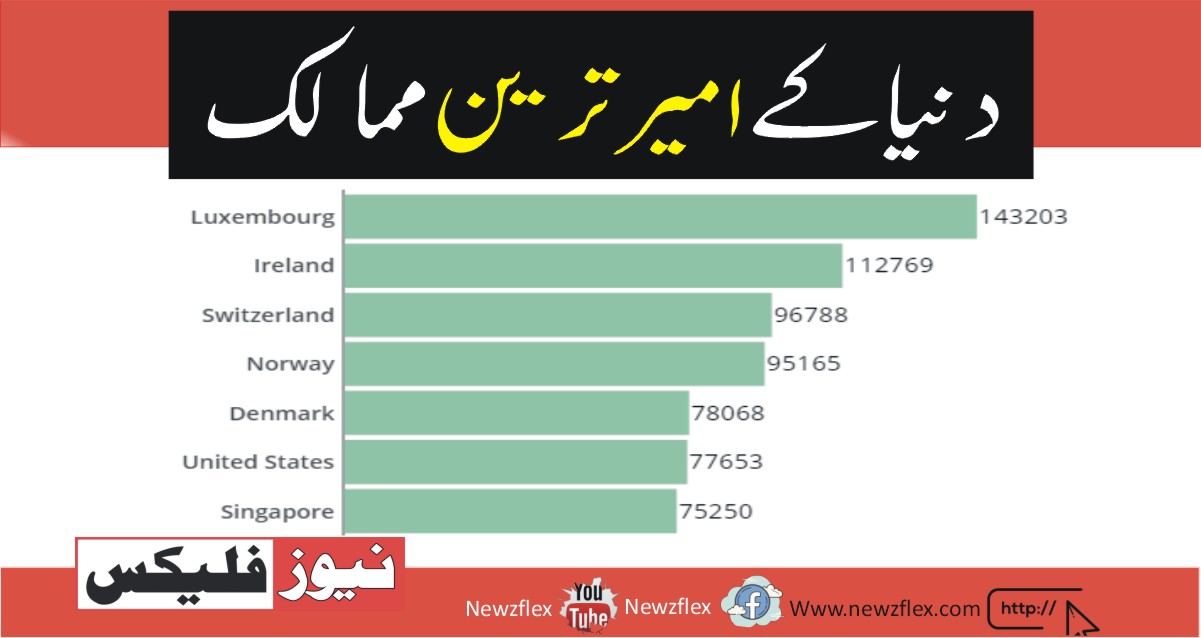
دنیا کے امیر ترین ممالک
فی کس جی ڈی پی – جبکہ یقینی طور پر یہ ایک نامکمل اقدام ہے تاہم ایک ملک کے معیار زندگی کی پیمائش کے لیے ایک مفید پراکسی ہے۔ ہم نے اپنے مشہور آرٹیکل کو اپ ڈیٹ کرنے اور 132 ممالک کے لیے اپنی پیشن گوئی پر ایک اور نظر ڈالنے کا فیصلہ کیا ہے جس کو دیکھنے کے لیے 2025 میں فی کس سب سے زیادہ جی ڈی پی کیا ہو گی ، اقتصادی تھنک ٹینک اور پیشہ ورانہ اقتصادی پیش گوئی کرنے والی فرمیں۔
چھوٹی یورپی قومیں اپنے انتہائی مضبوط اداروں ، مستحکم پالیسی ماحول اور اعلیٰ کارکردگی کے حامل تعلیمی نظام کی بدولت رینکنگ پر حاوی ہیں ، جس میں امریکہ اور سنگاپور سرفہرست سات ممالک میں شامل ہیں۔
نمبر1. لکسمبرگ: 2025 میں 143،203 ڈالر فی کس۔

نمبر1. لکسمبرگ: 2025 میں 143،203 ڈالر فی کس۔
ہم نے پیش گوئی کی ہے کہ 2025 میں برائے نام جی ڈی پی شرائط (مارکیٹ ایکسچینج ریٹ پر) میں لکسمبرگ دنیا کی امیر ترین معیشت ہوگی۔ حالیہ دہائیوں میں لگزمبرگ کی معاشی کامیابی خدمات کے شعبے میں تیزی کی بدولت ہے: یہ ملک یورپی یونین کے کئی اہم اداروں کا گھر ہے اور ایک سازگار ٹیکس حکومت کی بدولت ایک بڑے مالیاتی شعبے کا حامل ہے۔
اگرچہ ممکنہ طور پر گزشتہ سال کوویڈ 19 کی وجہ سے معیشت سکڑ گئی تھی ، اسے آنے والے سالوں میں مضبوط ترقی کی راہ پر لوٹنا چاہیے اور خدمات کے شعبے کی مسلسل حرکیات اور مضبوط آبادی میں اضافے کے درمیان ، یورپی یونین کی اوسط سے بھی اوپر بڑھنا ہے۔
لکسمبرگ دنیا کے سب سے بڑے مالیاتی مراکز میں سے ایک ہے ، جس کی وجہ ‘گرانڈے ریجن’ کی مشہور ہنر مند مزدور اور بدنام ٹیکس ریگولیشن ہے۔ یہ انویسٹمنٹ فنڈ انڈسٹری میں دنیا بھر میں رہنما ہے جس کے اثاثے( ای یو آر4.1ٹی آر این )سے زیادہ کے زیر انتظام ہیں۔
یہ یورپ کا سب سے بڑا بین الاقوامی نجی بینکنگ سینٹر اور سب سے بڑا کیپٹی ری انشورنس سینٹر بھی ہے۔ لگزمبرگ میں تقریبا 3، 3،900 فنڈز رجسٹرڈ ہیں۔ 2018 تک لکسمبرگ میں بینکوں کی تعداد 133 تھی جن میں سے 40 غیر ملکی بینکوں کی شاخیں ہیں۔ اجتماعی طور پر ، بینکوں کے اثاثے تقریبا 760 یورو ہیں۔ – کیتھرینا کوئنز ، آکسفورڈ اکنامکس کی ماہر معاشیات۔
نمبر2. آئرلینڈ: 2025 میں 112،769 ڈالر فی کس

نمبر2. آئرلینڈ: 2025 میں 112،769 ڈالر فی کس۔
حالیہ دہائیوں میں ، آئرلینڈ یورپی یونین کے غریب ترین ممالک میں سے ایک امیر ترین ملک بن گیا ہے ، ایک برآمد پر مبنی معاشی ماڈل اور خاص طور پر بڑی کثیر القومی کمپنیوں کی طرف سے ایف ڈی آئی کو راغب کرنے میں بڑی کامیابی کی بدولت ایسا ممکن ہوا۔ آئرلینڈ کو ایک سازگار ٹیکس حکومت ، ایک ہنر مند ، انگریزی بولنے والی افرادی قوت ، ایک مستحکم کاروباری ماحول اور امریکہ کے ساتھ قریبی تعلقات سے ہماری پیش گوئی کے افق پر فائدہ ہوتا ہے ۔
آئرلینڈ ایک صحت مند کلپ پر بڑھتا ہی جارہا ہے ، جس کی مضبوط اندرونی نقل مکانی اور سرمایہ کاری سے تقویت پائی جاتی ہے۔ تاہم ، بریگزٹ کی وجہ سے برطانیہ کے ساتھ اضافی تجارتی تنازعات ، اور ملک کی ٹیکس مسابقت میں ممکنہ کمی خطرات پیدا کرتی ہے۔ مزید یہ کہ ملک میں کثیر القومی اداروں کی بڑی موجودگی کی وجہ سے قومی اکاؤنٹس کے اعداد و شمار کی تشریح مشکل ہو گئی ہے۔
‘آئرلینڈ کی اقتصادی ترقی کا حساب لگانا آئرلینڈ میں واقع غیر ملکی ملٹی نیشنل کمپنیوں کی بیلنس شیٹ کی نقل و حرکت کے مسخ شدہ اثرات سے پیچیدہ ہے۔ ان بگاڑ کا مطلب یہ ہے کہ آئرلینڈ کے سرکاری جی ڈی پی کے اعداد و شمار گھریلو سرگرمیوں کا ناقابل اعتماد پیمانہ ہیں ، جبکہ یہ غیر مستحکم بھی ہے اور بار بار اور خاطر خواہ نظر ثانی کے تابع ہے۔
یہ خاص طور پر بیرونی شعبے میں شدید حد تک ہے ، جہاں بڑے کارپوریشنوں کی بیلنس شیٹ کی نقل و حرکت کی وجہ سے وبائی امراض کے دوران سرکاری برآمدات میں اضافہ ہوا ہے۔ دواسازی اور ٹیکنالوجی فرمیں جو آئرلینڈ کے کثیر القومی شعبے پر حاوی ہیں اس طرح اب تک نسبتا بہتر کارکردگی کا مظاہرہ کر رہی ہیں۔
اس بہتر برآمدی کارکردگی کے ساتھ ساتھ حکومتی اخراجات میں اضافہ اور درآمدات میں دو ہندسوں میں کمی کا اندازہ لگایا گیا ہے کہ حقیقی نجی کھپت اور مجموعی طور پر مقررہ سرمایہ کاری میں متوازن توازن میں کمی آئی ہے۔ – اکانومسٹ انٹیلی جنس یونٹ
نمبر3. سوئٹزرلینڈ: 2025 میں 96،788 ڈالر فی کس

نمبر3. سوئٹزرلینڈ: 2025 میں 96،788 ڈالر فی کس۔
سوئٹزرلینڈ کی معیشت کو ایک انتہائی مضبوط ادارہ جاتی فریم ورک ، ایک مستحکم اور سازگار کاروباری ماحول ، اور ایک انتہائی اعلی کارکردگی کا حامل تعلیمی نظام کی مدد حاصل ہے۔ یہ ملک یورپ کی سب سے بڑی قومی منڈیوں کے مرکز میں ایک مضبوط صنعتی اڈے اور ایک آسان مقام کا حامل ہے۔
سوئٹزرلینڈ نے کوویڈ 19 کے بحران کو کافی حد تک برداشت کیا ، فراخدلانہ ریاستی تعاون اور عام طور پر دیگر ممالک کے مقابلے میں نرم پابندیوں عمل میں لائی گئیں۔ آگے بڑھتے ہوئے ، معیشتک امیابی کی طرف لوٹتی ہوئی نظر آتی ہے – اگرچہ یورپی یونین کے ساتھ دوطرفہ تعلقات اور بیرونی جھٹکے کے سامنے آنے سے اختلافات کے خطرات پیدا ہوئے ہیں۔
سنہ2019 کے آخر میں صورتحال کے مقابلے میں ، تیسری سہ ماہی کے اختتام پر سوئٹزرلینڈ میں سرگرمی کی سطح اس کے یورپی پڑوسیوں کے مقابلے میں بہت زیادہ تھی -مجموعی طور پر 2020 کے لیے ، ہم جی ڈی پی کے 3.2 فیصد کے سکڑنے کی پیش گوئی کرتے ہیں۔ 2021 میں بحالی ٹھوس ہونی چاہیے ، بنیادی طور پر سال کے دوسرے نصف حصے میں جب کوویڈ ویکسین وبائی امراض کی تیسری لہر کے کسی بھی خطرے کو ختم کردیتی ہے۔ ہم سال 2021 میں مجموعی طور پر 3.1 فیصد اضافے کی توقع رکھتے ہیں۔ شارلٹ ڈی مونٹپیلیئر ، آئی این جی کے ماہر معاشیات۔
نمبر4. ناروے: 95،165 امریکی ڈالر فی کس

نمبر4. ناروے: 95،165 امریکی ڈالر فی کس۔
1960 کی دہائی میں شمالی سمندر میں تیل اور گیس کی دریافت نے ناروے کی معیشت کو بدل دیا ، حکومت نے بعد میں دنیا کا سب سے بڑا خودمختار دولت فنڈ تعمیر کیا – جس کی قدر آج قدرتی وسائل کی دولت کے پیچھے 1 ٹریلین ڈالر سے زیادہ ہے۔ آج ، توانائی اب بھی معیشت کا ایک اہم جزو ہے ، حالانکہ خدمات کا شعبہ جی ڈی پی کے 60 فیصد سے زیادہ پر اب تک کا سب سے بڑا معاشی شعبہ ہے۔ دیگر یورپی معیشتوں کے مقابلے میں ناروے کوویڈ 19 سے کم متاثر ہوا تھا ، اور تیل کی قیمتوں میں اضافے اور گھریلو طلب میں اضافے کی بدولت 2021 کے بعد سے ترقی کی طرف لوٹنا ہے۔
‘ہم توقع کرتے ہیں کہ گھریلو ناروے کی معیشت مضبوط بحالی کی پوزیشن میں ہوگی- وبائی امراض کے دوران گھریلو آمدنی اچھی رہی ہے ، بڑے حصے میں حکومت کی طرف سے بے روزگاری کی مدد کی بدولت۔ پچھلے سال صارفین کے اخراجات میں کمی آئی کیونکہ گھروں نے سفر اور خدمات کو ختم کردیا۔ لیکن صارفین کا اعتماد اچھا ہے ، سامان کی کھپت مضبوط رہتی ہے ، اور ہاؤسنگ مارکیٹ میں تیزی آرہی ہے۔
لہذا ہم سمجھتے ہیں کہ صارفین کی بنیادی مانگ مضبوط ہے اور پابندیاں ختم ہونے کے بعد معاشی بحالی میں نمایاں کردار ادا کرے گی۔ کاروباری ادارے حکومت کی سخاوت سے بھی فائدہ اٹھا رہے ہیں ، جس نے دیوالیہ پن میں کسی بھی اضافے کو روکا ہے۔ مزید یہ کہ تیل کی صنعت کے لیے عارضی ٹیکس تبدیلیوں نے کمپنیوں کے سرمایہ کاری کے منصوبوں کو حوصلہ دیا ہے اور اس شعبے میں سرگرمیوں میں بڑی کمی کو روکا ہے۔ – سویڈ بینک کے تجزیہ کار۔
نمبر5. ڈنمارک: امریکی ڈالر فی کس 78،068

نمبر5. ڈنمارک: امریکی ڈالر فی کس 78،068۔
معیشت کے اعلیٰ معیار زندگی کو موثر حکمرانی ، بلند انسانی سرمائے اور سازگار کاروباری ماحول سے معلوم کیا جا سکتا ہے۔ ڈنمارک ایک ترقی یافتہ سروسز سیکٹر ہے ، خوراک کا خالص برآمد کنندہ ہے اور 2050 تک کاربن نیوٹرل جانے کے حکومتی ہدف کے ایک حصے کے طور پر قابل تجدید توانائی کی صنعت کا حامل ہے۔ ہماری پیش گوئی کے افق پر ترقی کی رفتار ، سازگار آبادیات اور صحت مند کھپت اور سرمایہ کاری سے متاثر۔ اس نے کہا ، بلند گھریلو قرض ایک خطرہ ہے۔
‘ہم نے حال ہی میں اپنی آبادی کی پیشن گوئی پر نظر ثانی کی ہے ، تارکین وطن کی مضبوط آمد اور لیبر فورس میں اصلاحات کو مدنظر رکھتے ہوئے جو کہ 2022 تک پنشن کی عمر 65 سے 67 تک بڑھ جائے گی۔ ہنر مند امیگریشن کا مزید خیرمقدم کرنے میں مزید مدد کرنی چاہیے۔
بڑھتی ہوئی شراکت کی شرح ، خاص طور پر پرانے کارکنوں میں ، ممکنہ پیداوار میں اضافے کے لیے توازن روزگار کی بڑھتی ہوئی شراکت کے پیچھے اہم عنصر ہے۔ اس سے اعلی ممکنہ نمو کو سہولت ملنی چاہیے۔ – روری فینیسی ، آکسفورڈ اکنامکس کے ماہر معاشیات۔
نمبر6. ریاست ہائے متحدہ امریکہ: 77،653 امریکی ڈالر فی کس

نمبر6. ریاست ہائے متحدہ امریکہ: 77،653 امریکی ڈالر فی کس۔
بہت سے جدید تکنیکی شعبوں میں ایک اہم پوزیشن ، گہری سرمایہ مارکیٹ ، ایک لچکدار لیبر مارکیٹ اور قانون کی مضبوط حکمرانی وہ تمام عوامل ہیں جو فی کس جی ڈی پی کے لحاظ سے امریکہ کو دنیا کے امیر ترین ممالک میں سے ایک بناتے ہیں۔
یہی عوامل اگلے کئی سالوں میں معیشت کو سہارا دیتے رہیں اور اس بات کو یقینی بنائیں کہ امریکہ دنیا کے امیر ترین ممالک میں رہے ، جبکہ وسیع مالی محرک کو مزید فروغ دینا چاہیے۔ تاہم ، ایک تلخ تقسیم شدہ سیاسی منظر نامہ ، قرضوں کی بلند سطح ، تیز سماجی و اقتصادی عدم مساوات اور چین کی کشیدگی سب کے نقطہ نظر کوہوا دیتی ہے۔
امریکی معیشت کی تنوع ، حرکیات اور مسابقت کے ساتھ ساتھ امریکی ڈالر کی اہم بین الاقوامی ریزرو کرنسی کی حیثیت اور امریکی ٹریژری مارکیٹ کی بہت بڑی جسامت اور گہرائی ، بڑھتے ہوئے مالی دباؤ کو دور کرتی رہے گی۔ تاہم ، امریکہ ‘ مالی طاقت بگڑ رہی ہے اور توقع ہے کہ وقت کے ساتھ اس بگاڑ میں تیزی آئے گی کیونکہ بڑھاپے سے متعلقہ حقدارانہ اخراجات ، قرضوں کی ادائیگی اور نسبتا کمزور حکومتی محصولات مسلسل مالیاتی خسارے کو بڑھاتے ہیں۔
اس اعتماد کو کم کرتے ہوئے کہ امریکی پالیسی ساز آئندہ برسوں میں وفاقی حکومت کے بجٹ کے خسارے کو کم کرنے کے لیے موثر اقدامات کریں گے اور قرضوں کے بوجھ میں مسلسل اضافہ مالیاتی اور ادارہ جاتی طاقت دونوں کے خاتمے کا اشارہ دے گا۔ – موڈیز کے تجزیہ کار۔
نمبر7. سنگاپور: امریکی ڈالر 75،250 فی کس

نمبر7. سنگاپور: امریکی ڈالر 75،250 فی کس۔
سنہ1965 میں ملائیشیا سے نکالے جانے کے بعد ، سنگاپور کی آزاد جمہوریہ تیسری دنیا کا ایک چھوٹا ملک تھا ، جس میں قدرتی وسائل نہیں تھے اور نسلی کشیدگی نہیں تھی۔ نصف صدی کو تیزی سے آگے بڑھایا ، اور سنگاپور فی کس شرائط کے لحاظ سے دنیا کے امیر ترین ممالک میں شامل ہے ، کئی دہائیوں سے برآمد پر مبنی ترقی کی بدولت جس نے جسمانی اور انسانی سرمائے میں بھاری سرمایہ کاری اور عالمی معیار کے کاروباری ماحول کی تخلیق دیکھی۔
اگرچہ 2020 میں سنگاپور کوویڈ 19 کی وجہ سے معیشت کی کھلی نوعیت کی وجہ سے نسبتا ً زیادہ متاثر ہوا تھا ، 2021 کے بعد سے معاشی سرگرمیاں تیزی سے بحال ہونی چاہئیں ، ہماری پیش گوئی کے افق پر دیگر ترقی یافتہ معیشتوں کے مقابلے میں خاصی تیزی سے ترقی کی توقع ہے۔ طویل مدتی پالیسی سازی پر توجہ دیں۔ تاہم ، مزید ڈیگلوبلائزیشن اور لیبر فورس کی نمو میں تیزی سے سست روی آؤٹ لو کے لیے خطرات پیدا کرتی ہے۔
The Richest Countries in the World
GDP per capita—while certainly an imperfect measure—is a useful proxy for measuring a country’s standard of living. We decided to update our popular article and take another look at our forecasts for the 132 countries we cover to determine which is able to have the highest GDP per capita in 2025.
The projections are Consensus Forecasts supported by the individual forecasts of over 1000 world-renowned investment banks, economic think tanks, and professional economic forecasting firms.
Small European nations dominate the ranking, because of their extremely robust institutions, stable policy environments, and high-performing education systems, with the US and Singapore rounding out the top seven.
1. Luxembourg: USD 143,203 per capita in 2025
We forecast Luxembourg to be the world’s wealthiest economy in 2025 in nominal GDP terms (at market exchange rates). Luxembourg’s economic success in recent decades is because of a booming services sector: The country is home to many important EU institutions and boasts a large financial sector due to a good tax regime.
While the economy likely contracted last year because of COVID-19, it should return to a robust growth trajectory within the coming years and is about to expand well above the EU average, amid the continued dynamism of the services sector and powerful growth.
Luxembourg is one of the world’s largest financial centres, thanks to renowned high-skilled labour from the ‘Grande Region’ and infamous tax regulation. it’s a worldwide leader within the investment fund industry with assets under management of over EUR4.1trn. it’s also the biggest international private banking centre and therefore the largest captive reinsurance centre in Europe.
There are approximately 3,900 funds registered in Luxembourg. As of 2018, the number of banks in Luxembourg was 133, of which 40 are branches of foreign banks. Collectively, the banks hold assets of roughly EUR760bn.- Katharina Koenz, an economist at Oxford Economics
2. Ireland: USD 112,769 per capita in 2025
In recent decades, Ireland has gone from being one of the poorest EU nations to 1 of the wealthiest, because of an export-oriented economic model and big success in attracting FDI—particularly from large multinationals.
Ireland benefits from a good tax regime, a skilled, English-speaking workforce, a stable business environment, and close ties to the U.S. Over our forecast horizon, Ireland is ready to continue growing at a healthy clip, bolstered by strong inward migration and investment.
However, extra trade frictions with the United Kingdom because of Brexit, and a possible reduction in the country’s tax competitiveness pose risks. Moreover, interpreting national account data is created difficult because of the massive presence of multinationals within the country.
Calculating Ireland’s economic process is complicated by the distortionary effects of balance-sheet movements of foreign multinational companies headquartered in Ireland. These distortions mean that Ireland’s official GDP figures are an unreliable measure of domestic activity, while also being volatile and subject to frequent and substantial revisions.
this can be particularly acute within the external sector, where official export growth figures have increased during the pandemic, as a result of large corporations’ balance-sheet movements. The pharmaceutical and technology firms that dominate Ireland’s multinational sector have so far fared relatively well.
This improved export performance, in addition to increased government spending and a double-digit decline in imports, is estimated to own quite counterbalanced sharp declines in real private consumption and overall fixed investment.- Economist Intelligence Unit
3. Switzerland: USD 96,788 per capita in 2025
Switzerland’s economy is supported by an especially robust institutional framework, a stable and conducive business environment, and an especially high-performing education system. The country also boasts a powerful industrial base and a convenient location at the guts of Europe’s largest national markets.
Switzerland weathered the Covid-19 crisis fairly well, due to generous state support and usually laxer restrictions than other nations. Looking forward, the economy is seen returning to a solid—if unspectacular—growth trajectory, although disagreements with the EU over the bilateral relationship and exposure to external shocks pose risks.
Compared to matters at the end of 2019, the extent of activity in Switzerland at the end of the third quarter was well above that of its European neighbour. For 2020 as a full, we forecast a contraction of three 2% of GDP.
The recovery in 2021 should be solid, mainly within half of the year once the COVID-19 vaccine eliminates any risk of a 3rd wave of the pandemic. We expect growth of three 1% for the year 2021 as a full. – Charlotte de Montpellier, an economist at ING
4. Norway: USD 95,165 per capita
The discovery of oil and gas within the sea in the 1960s transformed Norway’s economy, with the govt. subsequently building the world’s largest sovereign wealth fund—today valued at over USD 1 trillion—on the back of this resource wealth.
Today, energy continues to be a key component of the economy, although the services sector is far and away from the largest economic sector at over 60% of GDP. Norway was less suffering from COVID-19 than other European economies and is ready to return to growth from 2021 onwards due to higher oil prices and rebounding domestic demand.
We expect the domestic Norwegian economy to be in position for a powerful rebound. Household incomes have maintained well during the pandemic, in large part because of generous unemployment support from the govt. Consumer spending fell last year as households reduced on travel and services. But consumer confidence is sweet, consumption of products remains strong, and also the housing market is booming.
We, therefore, believe that underlying consumer demand is powerful and can contribute significantly to the economic recovery once restrictions are lifted. Businesses also are benefitting from generous government support, which has prevented any rise in bankruptcies. Moreover, temporary tax changes for the oil business have spurred companies’ investment plans and prevented an even bigger decline in activity within the sector.- Analysts at Swedbank
5. Denmark: USD 78,068 per capita
The economy’s high standard of living is often traced to effective governance, elevated human capital, and a conducive business environment. Denmark features a developed services sector, could be a net exporter of food, and boasts a burgeoning renewable energy industry as a part of the government’s goal to travel carbon neutral by 2050.
Despite taking a knock in 2020 from the coronavirus pandemic, the economy should resume a strong growth trajectory over our forecast horizon, buttressed by favourable demographics and healthy consumption and investment. That said, elevated household debt could be a risk.
We have recently revised our population forecasts, taking into consideration stronger inflows of migrants and labour force reforms that will see the pension age increase from 65 to 67 by 2022. This has helped raise the potential of the Danish economy, and also the new government’s arrangement to be more welcoming of skilled immigrants should help further.
A rising participation rate, particularly among older workers, is the main factor behind the increased contribution of equilibrium employment to potential output growth. this could facilitate higher potential growth. – Rory Fennessy, an economist at Oxford Economics
6. United States: USD 77,653 per capita
A leading position in many cutting-edge technological fields, deep capital markets, a versatile marketplace, and a powerful rule of law are all factors that make the United States one of the richest countries in the world in GDP per capita terms.
These same factors should still support the economy over the subsequent several years and make sure the U.S. remains among the world’s wealthiest nations, while vast fiscal stimulus should provide an extra boost. However, a bitterly divided political panorama, elevated debt levels, sharp socioeconomic inequalities, and China tensions all cloud the outlook.
The diversity, dynamism, and competitiveness of the U.S. economy, together with the U.S. dollar’s status because of the preeminent international reserve currency and the extremely large size and depth of the U.S. Treasury market, will still offset rising fiscal pressures.
However, the U.S.’ fiscal strength is deteriorating and deterioration is anticipated to accelerate over time as higher ageing-related entitlement spending, debt service payments and comparatively weaker government revenues drive persistent fiscal deficits.
Diminishing confidence that U.S. policymakers will take effective action within the coming years to cut back centralized budget deficits and also the ongoing rise of the debt burden would signal an erosion of both fiscal and institutional strength. – Analysts at Moody’s
7. Singapore: USD 75,250 per capita
Upon expulsion from Malaysia in 1965, the nascent independent republic of Singapore was a small third-world country, with no natural resources and simmering ethnic tensions. Fast forward half a century and Singapore is now among the world’s richest nations in per capita terms, due to decades of export-oriented growth which saw heavy investments in physical and human capital and therefore the creation of a world-class business environment.
While Singapore was relatively hard-hit in 2020 by COVID-19 because of the economy’s open nature, economic activity should recover swiftly from 2021 onwards, with growth expected to be notably faster than most other developed economies over our forecast horizon, aided by the government’s target long-term policymaking. However, further deglobalization and a rapid slowdown in labour force growth pose risks to the outlook.
The [2021] Budget will aim to make three enablers,
(1) Promoting innovation and collaboration on a world scale,
(2) Providing capital to businesses, and
(3) Developing workers’ skills, talents, and creativity.
More clarity on Singapore Green Plan 2030 is seen likewise. The COVID-19 pandemic has prompted significant global shifts on the economic and social fronts, accelerated technological advances, and created new global domains for competition and cooperation.
Budget 2021, titled “Emerging Stronger Together”, will serve to permit the govt. to be a key enabler supporting Singapore’s recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic, further invest in economic transformation and position Singapore for achievement within the long term. – Barnabas Gan, economist at United Overseas Bank.








When will pakistan come top of . the list of richest country
It is possible only with true patriotism and fair dealings.As Pakistani we should try to play our role only.